Success in the competitive market of 2026 frequently depends on how fast businesses adjust. Without clear direction, leading a scaling company can seem overwhelming to some leaders. That reality explains the shift—what once seemed optional now stands essential: ERP tools are no longer extras for smaller operations. Instead, they anchor daily functions.
A network of coordinated functions defines how modern businesses manage operations. Through integration, financial data flows together with workforce records under one platform. Cloud-based systems now allow access without reliance on physical servers. Efficiency, once limited to large organizations, is available even at smaller scales.
Today’s focus lands on the top ERP systems suited to small enterprises by 2026. Examination follows regarding their role in refining operations while supporting sustained financial health.
Key Takeaways: Best ERP Software for Small Businesses 2026
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software must be able to expand with your company in order to avoid future expensive migrations.
- The top ERP software for small businesses should be able to integrate with your current CRM and communication software.
- Small businesses should focus on AI ERP to gain the power of predictive analytics and forecasting.
- A successful ERP implementation strategy should be based on well-defined goals and executive buy-in.
What is ERP software?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a centralized software application that integrates all important aspects of a business in one database. It integrates all departments of a business, such as finance, sales, and human resources, to ensure a smooth flow of information.
Moreover, it replaces disparate legacy applications with real-time visibility of data. As a result, it allows decision-makers to make decisions based on accurate information. Today, ERPs use the power of the cloud to offer accessibility to a growing workforce.
Why ERP Software is Essential for Small Businesses in 2026
In today’s business world, there is a need for a unified approach to data management to achieve business sustainability. Some strategic advantages of moving away from legacy solutions to modern ERP software are:

- Eliminating data fragmentation: Moving away from using disparate data sources, such as spreadsheets, to using a single version of the truth eliminates human error.
- Real-time operational visibility: Using a unified version of the truth is the first step to gaining immediate visibility into all areas of the business.
- AI-driven administrative efficiency: With the advent of AI ERP software for small businesses, there is now automation for more efficient administration.
The Ultimate List: 15 Best ERP Software for Small Businesses
Comparison Table: Top ERP Software for Small Businesses
ERP Software | Key ERP Features | Starting Price (2026) |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Cetec ERP |
QMS, shop floor control, MRP, mobile scanning, real-time production tracking |
$50/user/mo + $650-$3200 company fee |
|
2. MRPeasy |
Visual scheduling, MRP, BOM, QuickBooks/Xero sync, cost estimation |
€39-49/user/mo |
|
3. VOGSY |
Resource management, project tracking, real-time forecasting, Google Data Studio |
$14/user/mo (Standard), $56 Enterprise |
|
4. Fulfil |
Multi-channel inventory sync, WMS, vendor management, automated returns |
Custom quote |
|
5. Versa Cloud ERP |
Multi-warehouse, e-commerce/POS, supply chain, CRM, landed cost calc |
Quote-based |
|
6. DualEntry |
With artificial intelligence aiding record keeping, financial tracking becomes continuous. |
Subscription (demo quote) |
|
7. SAP Business One |
MRP, inventory management, financials, HANA analytics, global tax support |
€38-91/user/mo |
|
8. Zoho Creator |
Low-code app builder, mobile apps, workflow automation, Zoho integration |
€8-25/user/mo |
|
9. Acumatica |
Consumption pricing, mobile apps, field service, custom reporting |
Usage-based |
|
10. ERPNext |
Open-source tools for HR, CRM, inventory, manufacturing projects, and Gantt Charts |
$5/mo (small), $200/mo (enterprise) |
|
11. WhereFour |
Recall management, recipe estimation, real-time planning, and compliance reporting |
Custom quote |
|
12. Deltek |
Project accounting, resource planning, compliance tracking, time/expense |
Quote-based |
|
13. Priority |
Mobile app builder, supply chain, CRM, automated workflows |
Quote-based (modules/users) |
|
14. Microsoft Dynamics 365 BC |
Excel/Teams/Power BI integration, AI forecasting, Copilot automation |
$80/user/mo (Essentials), $110 Premium |
|
15. Odoo |
40k+ apps, CRM/sales/inventory, website builder, AI lead scoring, POS |
€14.90-22.40/user/mo |
Operating across borders requires decisions guided by evidence. To receive curated analysis on worldwide supply chains and expansion overseas, access the leadership summary, subscribe to Digest.Pro.
1. Cetec ERP

Cetec ERP is an enterprise-wide solution for all aspects of manufacturing and distribution, built from scratch as a cloud-native system. It integrates all stages of the manufacturing cycle, from quoting through shipping. Additionally, it has many features concerning compliance with regulations and is considered a suitable ERP system for the industry.
Best for: Small producers in regulated industries such as defense, aerospace, and medicine.
Key Features:
- Integrated shop floor control and material requirements planning.
- Real-time production tracking and automatic purchases.
- Mobile scanning and native barcoding.
Pricing: There are 3 tiers: The Lite plan costs $50, the Standard costs $50 per user/month + $650 per company, and the Enterprise plan goes for $50 per user/month + $3200 per company/month.
Pros:
- Exceptionally affordable for a high-end manufacturing system.
- Built-in compliance features for ISO and AS9100.
- A browser-based interface requires zero local installation.
- Strong traceability for raw materials and finished goods.
- Excellent technical support for complex deployments.
Cons:
- The user interface is data-heavy and utilitarian.
- Requires a disciplined approach to inventory data entry.
Read more: 20 Best Kanban Tools To Improve Workflow Efficiency In 2026
2. MRPeasy

MRPeasy is a production planning system driven by AI that places an emphasis on user adoption and ease of use. It gives small manufacturers a level of visibility that is typically only available to large corporations. It also closes the gap between industrial-scale enterprise resource planning and basic accounting.
Best for: Small manufacturing companies that require visual planning and employ 10 to 200 people.
Key Features:
- The system shows production schedules and operational calendars through its visual display system for shop floor management.
- ERP automates Material Requirements Planning (MRP).
- Connectivity with QuickBooks Online and Xero.
Pricing: Price depends on how many users will work with MRPeasy, but it starts from €39/user.
Pros:
- Rapid implementation, usually delivered in weeks.
- Modern and intuitive interface for reduced staff training times.
- Robust ERP for tracking lots and inventory in small businesses.
- Precise cost estimation using labor hours and BOM.
Cons:
- Limited functionality for massive, multi-location global logistics.
- Has no built-in human capital management (HCM) modules.
- Restricted personalization, in contrast to open-source alternatives.
3. VOGSY

The professional services automation (PSA) solution VOGSY was created from the ground up with the express purpose of operating within the Google Workspace ecosystem. VOGSY manages the complete ‘Quote-to-Cash’ lifecycle within a familiar space, and it also takes advantage of Google Drive and Sheets to make sure project data is available at all times.
Best for: Consultancies, agencies, and small service-oriented businesses that use Google Workspace.
Key Features:
- Integrated resource management and project tracking are important features.
- In real-time financial forecasting, margin analysis, etc.
- Automatic invoicing and expense tracking using Gmail.
- Intelligent project templates for recurring services.
- native reporting integration with Google Data Studio.
Pricing: The standard plan costs $14 per user/month, ‘Full user’ goes to $28, and the most advanced plan expenses $56 per user/month.
Pros:
- Zero learning curve for dedicated Google Workspace users.
- Deep visibility into project profitability and billable hours.
- Highly cost-effective compared to standalone ERPs.
Cons:
- Not suitable for businesses dealing with physical manufacturing.
- Highly dependent on the Google ecosystem for functionality.
4. Fulfill

Fulfil is an ERP and Operations Management System (OMS) made for rapidly expanding e-commerce companies. Its main goal is to integrate inventory and warehouse operations with multi-channel sales. As a result, it is regarded as one of the best cloud ERP programs available for contemporary online merchants.
Best for: High-volume online retailers expanding into several markets.
Key Features:
- Synchronization of inventory across multiple channels in real time.
- Sophisticated shipping integrations and warehouse management (WMS).
- Thorough vendor and purchase order management.
- Automated returns and exchange workflows.
Pricing: Custom quote-based; typically aimed at mid-market growth companies.
Pros:
- Exceptionally smooth integration with Shopify, Amazon, and Bigcommerce.
- API-first, modern architecture for adaptable data flow.
- A strong emphasis on lowering shipping errors and stockouts.
- Easily scales to high transaction volumes on holidays.
Cons:
- For very early-stage startups, it might be too costly.
- requires a large amount of setup time for intricate shipping regulations.
- The user interface may not be user-friendly for non-technical personnel.
- Long-term contracts may not sit well with flexible brands.
5. Versa Cloud ERP

Versa Cloud ERP is designed for companies that have moved beyond simple accounting software but do not require the full-scale functionality of enterprise-level solutions. This software provides advanced functionality in the areas of inventory, manufacturing, and worldwide financials. In addition, it provides exceptional functionality for managing multi-entity and multi-currency businesses for small global companies.
Best for: Growing distributors and manufacturers with complex inventory requirements.
Key Features:
- Multi-warehouse and multi-entity financial consolidation.
- It integrates e-commerce and POS.
- An advanced supply chain management and procurement tool.
- Comprehensive pricing rules for different customer tiers.
- Native CRM and lead management.
- Real-time calculation of land cost for international shipments.
Pricing: Quote-based.
Pros:
- Offers “big ERP” features at a small business price point.
- Solid multi-channel inventory capabilities.
- Dedicated mobile app for warehouse activities.
- Automated bank feeds that enable rapid financial reconciliation.
- Support for high-volume transactions without lag.
Cons:
- The interface can be complex for non-technical users.
- Customization options are fewer than open-source alternatives.
- The reporting engine requires a learning curve to master.
Managing global operations requires a data-driven strategy. For exclusive insights on cross-border logistics and international business scaling, subscribe to digest.pro.
6. DualEntry

DualEntry is focused on “reimagining” the accounting-first ERP solution for the digital era. Its primary goal is to help companies get financial clarity as quickly as possible. Furthermore, for finance teams, it also promises fast data entry and reconciliation.
Best for: Financially oriented businesses that need to do bookkeeping quickly.
Key Features:
- A rapid financial ledger with AI-assisted entry
- Real-time cash flow and profitability views
- Simplified vendor and customer management
Pricing: Subscription-based; pricing details provided upon demonstration.
Pros:
- Clean and distraction-free design for finance teams
- Fast implementation and data migration options
- Exceptional support for growing companies
Cons:
- Lacks the deep manufacturing modules found in systems like Cetec.
- The ecosystem of third-party integrations is still growing.
7. SAP Business One

SAP Business One is an integrated solution that offers a robust framework specifically designed for the small business sector. It focuses on data integrity and strict financial management for all organizational departments. Additionally, it is quite effective for businesses that want maximum technical visibility of their production and procurement cycles.
Best for: Small manufacturers and distributors needing precise, enterprise-grade control.
Key Features:
- Full Material Requirements Planning (MRP) functionality.
- Intensive ERP for small business inventory management.
- Advanced financial management with global tax support.
- Integrated customer services and helpdesk applications.
- SAP HANA real-time analytics.
Pricing: There are many options; for the small team tiers, it costs €38, €47, and €91 (for Standard, Limited, and Professional).
Pros:
- Best-in-class audit trails and financial accuracy.
- Extensive industry-specific vertical solutions.
- Excellent global support infrastructure for international logistics.
- Superior data security and integrity.
- Smooth scalability into larger SAP environments.
- Superb multi-currency and multi-language support.
Cons:
- The interface can feel more traditional than modern web apps.
- Requires disciplined data entry for maximum effectiveness.
- Higher upfront costs due to implementation partner fees.
Read more: Best AI Project Management Tools in 2026: Benefits, Key Features, and How to Choose
8. Zoho Creator

Zoho Creator is a low-code development tool that allows businesses to develop their own custom ERP tools. Zoho Creator offers a “Lego-like” approach to business automation, where you only build the modules you want. Plus, it natively integrates with all of the Zoho apps.
Best for: Businesses with unique business processes that don’t match any of the above ERPs.
Key Features:
- Drag-and-drop application builder with AI logic assistance.
- Native mobile app generation for all custom modules.
- Integrated analytics and data visualization.
- Sophisticated notification triggers and workflow automation.
Pricing: The standard plan costs €8, the professional plan goes for €20, and the enterprise plan for €25.
Pros:
- Complete adaptability to duplicate your precise workflow.
- Quick time to market for unique applications.
- Entry point for microbusinesses that is extremely reasonably priced.
- Completely connected with Zoho Books and CRM.
Cons:
- It requires some basic programming knowledge or logical thinking.
- You must build your own reporting and data structures.
9. Acumatica

Acumatica is a leader in cloud ERP software with its modern, browser-based approach. It beats its competitors with its unique pricing model. In contrast to determining costs by user, Acumatica is based on a consumption model. You only spend money on what you consume. This encourages all employees in a company to participate.
Best for: Mid-sized teams that prioritize mobile access and unlimited user counts.
Key Features:
- Consumption-based pricing that scales with transaction volume.
- Native mobile functionality for all business modules.
- Strong field service and construction-specific editions.
- Integrated document management with automated OCR.
- Powerful “Generic Inquiries” tool for custom reporting.
Pricing: Subscription-based; pricing is tailored to processing volume.
Pros:
- Better cross-functional team collaboration is ensured by unlimited users.
- Suitable deployment options on both public and private clouds.
- Excellent “connected business” architecture.
- Growing list of third-party ISV applications.
- Excellent customer success strategy.
Cons:
- The consumption-based model can be difficult to budget when growth is rapid.
- Training is essential, as it has a robust feature set.
- Implementation requires a specialized VAR.
- The product has a costly module activation model.
10. ERPNext

ERPNext is a powerful, open-source enterprise resource planning solution. It provides a full suite of applications covering everything from HR to manufacturing. Consequently, it is excellent, affordable ERP software for small business teams that have internal technical talent.
Best for: Technical startups and organizations wanting total control over their data.
Key Features:
- 100% open source with an enormous community of developers.
- Integrated HR, payroll, CRM, and inventory modules.
- Advanced manufacturing and maintenance management.
- Integrated asset management and depreciation tracking.
- Native project management with Gantt charts.
- Integrated customer website portal and help desk.
Pricing: For small businesses, the plan costs $5 per month; for medium and large enterprises, it goes for $200 per month
Pros:
- Excellent value for the quantity of features provided.
- Incredibly adaptable thanks to the “Custom Script” feature.
- The user interface is responsive, modern, and tidy.
- Transparent roadmap and community updates.
Cons:
- Self-hosting requires significant Linux and server expertise.
- Community support can be slower than dedicated paid SaaS.
- Documentation can be inconsistent for newer features.
This guide provides you with spotlight knowledge, but today’s market conditions require you to be aware and to have a holistic view of the market.
Subscribe to Digest.Pro to stay informed about new updates, releases, future trends, and game-changing technology.
11. WhereFour

WhereFour is specialized ERP software designed for the food and beverage industry. It places a strong emphasis on nutritional compliance and “farm-to-table” lot tracking. Additionally, its integration with common financial and online sales platforms supports cohesion between output and market demand. Unified data flow emerges through alignment with established business software.
Best for: Small bakeries and food and/or beverage manufacturers.
Key Features:
- sophisticated recall management and lot tracking.
- Cost tracking for formulation and recipes was integrated.
- scheduling of production and inventory in real time.
- automated reporting of compliance to regulatory agencies.
Pricing: Based on a custom quote.
Pros:
- Outstanding specialized functionality for audits and food safety.
- Production dashboards that are visually appealing and simple to use.
- robust mobile application for the shop floor and warehouse.
Cons:
- Limited usefulness for non-food manufacturing.
- Lacks native HR and heavy financial consolidated modules.
12. Deltek

Deltek is the gold standard for project-based businesses. While it serves massive government contractors, its mid-market offerings are ideal for project-centric small businesses. Profitability stays consistent across initiatives due to precise expense monitoring built into the system.
Best for: Architecture firms, consultancies, and government contractors.
Key Features:
- Advanced project accounting and revenue recognition.
- Integrated resource planning and talent management.
- Comprehensive compliance tracking for government audits.
- Real-time project health and profitability dashboards.
- Native time and expense tracking for mobile employees.
Pricing: Quote-based pricing tailored to firm size.
Pros:
- Unmatched depth in project-based financial management.
- Strong reporting on utilization and billable efficiency.
- Scalable for firms growing their government contract portfolio.
- Excellent support for complex billing and labor laws.
- Reliable data security for sensitive client projects.
Cons:
- Higher price point than general-purpose ERPs.
- Can feel overly complex for little service teams.
- The learning curve is steep for administrative personnel.
13. Priority
The flexible ERP system Priority is available for both on-premise and cloud deployments. Its main goal is to use integrated modules to present a “holistic” picture of the company. Furthermore, changes in demand are met without structural delays. The design supports movement between setups as needs shift. Performance remains consistent under varying circumstances.
Best for: Manufacturers and distributors in the small to medium market who require flexibility.
Key Features:
- Native mobile app builder for on-the-go management.
- Robust supply chain management and logistics.
- Integrated CRM and financial reporting.
- Automated workflow engine for custom business logic.
Pricing: Quote-based pricing according to modules and user count.
Pros:
- Very adaptable to particular industry workflows.
- Strong worldwide presence and multilingual support.
- Outstanding harmony between usability and depth.
- Quicker deployment cycles than those of legacy systems.
Cons:
- The ecosystem of third-party integrations is smaller than that of Odoo.
- Training documentation can be less detailed than competitors.
- User interface requires some time to master effectively.
14. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central

Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central’s main task is to serve as a centralized cloud environment for extensive enterprise resource management. It was developed to align financial, sales, and operational functions for small and medium businesses. Originally evolving from Microsoft Navision, the focus is on linking processes with accessible information flow.
Best for: Organizations heavily using Microsoft 365 tools while needing room to grow.
Key Features:
- Connectivity to native Excel, Outlook, and Teams applications.
- Automated financial processing through integration with Microsoft Copilot.
- Real-time business intelligence via Power BI Embedded.
- AI-based demand predictions to optimize inventory and cash management.
Pricing: Essentials tier for $80 per user/month, and Premium is available for $110 per user/month; also, there is a free trial.
Pros:
- Minimal learning curve for employees familiar with the Office interface.
- Automatic system updates without the risk of breaking custom settings.
- Massive global partner network for local support and implementation.
- Extensible functionality through the Microsoft AppSource marketplace.
- High-level data security is guaranteed by the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Cons:
- Initial implementation almost always requires a certified consultant.
- Licensing costs can be higher compared to basic accounting services.
- Few high-level capabilities demand extra Power Platform authorizations.
Read more: 15 Best Product Roadmap Tools for Stakeholder Alignment in 2026
15. Odoo

Odoo is a modular ERP software option designed to scale alongside your organization and created to unify various business functions globally. It offers a vast ecosystem of integrated apps that share a single database. This means you can jump straight into just one app and add more as your small business grows.
Best for: Good as ERP software for startups and innovators seeking a fully-fitted, modern digital stack in one place.
Key Features:
- Tons of community-made apps—over 40,000—for just about anything you need.
- CRM, sales, inventory, and accounting are all in one place.
- Website building and marketing tools together.
- AI helps you score leads and predict future sales.
- A POS system that works great for stores and restaurants.
- Cool tools for making things and keeping them in good shape.
- E-learning and hiring stuff built right in.
Pricing: The standard tier costs €14.90 per user/month, and the Individual tier goes for €22.40 per user/month; also, there is a free trial
Pros:
- Highly intuitive and modern user interface.
- Total flexibility to scale functionality as you grow.
- Massive library of integrations with external services.
- Excellent community support and regular feature releases.
- Mobile-first design for managing business on the move.
Cons:
- Costs can rise quickly as you add complex third-party modules.
- Custom code requires specialized Odoo developers.
- Some community modules may lack stability or support.
- Initial configuration can be complex without expert guidance.
Staying ahead in 2026 begins not only with tools but also with awareness. For receiving current perspectives on leading change in business technology, subscribe to Digest.pro.
Key ERP Features That Drive Efficiency in 2026
Executives need to be able to gauge certain modules that are impacting the bottom line. Today’s systems need to provide:
- Unified financials: Automated accounting ensures the balance sheets are always “audit-ready.”
- Strategic supply chain: In addition, real-time visibility avoids stockouts and optimizes procurement costs.
- Integrated CRM: This will ensure you build only what the market wants by aligning sales data with your production.
- AI analytics: The use of AI ERP assists small businesses in identifying trends for a proactive strategy.
Read more: 8 Best Open Source Product Management Software of 2026
How to Choose the Best ERP Software: Buyer’s Guide
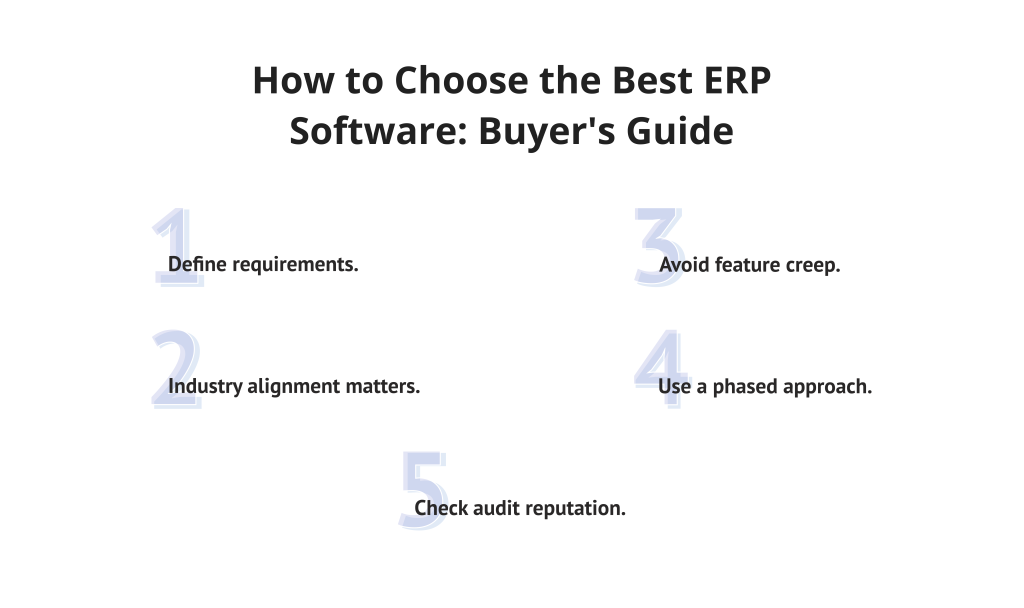
A choice of system carries significant consequences. Use the following method to assess options:
- Define requirements: Focus follows clarity in deciding where funds go. Priorities shape choices, not desires.
- Industry alignment: Ensure the vendor offers specialized ERP tools for your vertical.
- Avoid feature creep: Start slow when applying automation across operations, so complexity does not grow unchecked.
- Phased approach: Begins where money moves, then reaches toward how things are made and who works.
- Audit reputation: Verify vendor support history through independent peer reviews.
Trends in 2026: AI and Cloud ERP software for Small Businesses

The future of enterprise resource planning is defined by hyper-automation:
- Self-healing supply chains: AI automatically reorders stock when disruptions occur.
- Cloud security: Cloud ERP software provides stronger security protocols than private servers.
- Demand forecasting: Predict seasonal demand with over 90% accuracy.
- Narrowing the gap: Technology helps small firms compete with global corporations.
Conclusion
Selecting top ERP systems for small businesses by 2026 means weighing capability against ease of use. Choosing Odoo instead of Cetec ERP still leads to one outcome: aligning operations to support expansion. With proper ERP resources, teams gain strength in structure—forming a lasting foundation through technology.
The landscape of enterprise technology is evolving rapidly. Don’t navigate the transformation alone—subscribe to Digest.Pro to receive exclusive weekly deep dives into the tools and strategies shaping the future of small business.
FAQ: ERP Software for Small Businesses
Among tools for small enterprises, two stand out clearly. One comes from Oracle, known as NetSuite. Another emerges through Microsoft, labeled Business Central. Which fits better relies heavily upon the current scale and system needs.
Yes. One example is Odoo, which provides both a Community edition and a single-app free option. Another full-featured choice, especially suited for new businesses watching expenses, goes by the name ERPNext.
Yes. One example is Odoo, which provides both a Community edition and a single-app free option. Another full-featured choice, especially suited for new businesses watching expenses, goes by the name ERPNext.
Yes. With these tools, companies reduce mistakes caused by hand entry while growing operations smoothly. Efficiency rises when workflows become consistent and less dependent on individual effort.
When operations grow more intricate, so does the need for ERP among smaller enterprises. The vitality of these tools rises alongside organizational demands.
The stages include Discovery, Design, Development, Testing, Deployment, Training, and Ongoing Support. Executing each stage correctly ensures system stability.
Yes. Smaller businesses can use operational tools through Dynamics 365 Business Central. Though differing in size, these solutions originate from one shared environment.
No. Operating on a commercial license basis, this platform does not permit free use. Payment remains required regardless of company size or deployment method.
Well-suited by design, Odoo supports flexible setups. Shifting team sizes meet responsive handling through Zoho Creator. Clear navigation marks each platform distinctly. Costs rise only when use increases, avoiding preset tiers.
ERP implementation for small businesses and startups usually takes anywhere from three to six months to complete setup. When off-the-shelf cloud platforms replace tailored systems, timelines tend to shrink. With ready-made features enabling fast rollouts, momentum builds earlier in the process.
Our Methodology
To create this review, we evaluated dozens of ERP software solutions using a strict, four-pillar framework:
- Functional depth: Power of core modules such as supply chain management and finance.
- Scalability: The ability to scale from a startup phase to an enterprise level.
- UX: Tested the ease of use of the interface, as high adoption is critical to ROI.
- Integration: Availability of APIs and connections to professional tools.
References
- Gartner (2024). “Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP for Service-Centric Enterprises.”
- Siar Sarferaz (2025). “Implementing Agentic AI Into ERP Software.”
- Ahmadu Sanusi, Audu Husseni (2025). “Exploring the Opportunities and Challenges of Data Analysis with SAP: A Review of ERP Software Effectiveness.”
- Marcello Sequeira (International Journal of Scientific and Management Research Strategic, May 2025). “Analysis of Enterprise Resource Planning Software: A Case Study.”
- Hussain Abdul Nabi, Ali Abbas Hussain, Abdul Karim Sajid Ali, and Haroon Arif (The Asian Bulletin of Big Data Management Journal, 2025). “Data-Driven ERP Solutions Integrated with AI for Streamlined Marketing Operations and Resilient Supply Chain Networks.”
- Alan R. Peslak, Girish H. Subramanian & George E. Clayton (2016). “The Phases of ERP Software Implementation and Maintenance: A Model for Predicting Preferred ERP Use.”
- Januari Pri Harsant, Sony Warsono (2026). “Determinants of ERP Adoption in the Food and Beverage Industry: Evidence from UTAUT2.”